

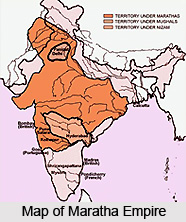
Goel, Sita Ram, Perversion of India’s Political Parlance.Hindu culture and Hindu history mean nothing to it except some catch-phrases or patriotic rhetoric for collecting crowds and securing votes.’ Hinduism for it is no more than a political card to be played for getting into power. Like its predecessor, it has neither knowledge nor appreciation of Hindu spiritual vision, or Hindu culture, or Hindu history, or Hindu social philosophy. The Hindu leadership at present can be easily compared to the Maratha leadeship which came to the fore after the Third Battle of Panipat (1761).Theory and practice of Muslim state in India. If they are asked to help one in distress, they will forget themselves in their haste to render assistance. to their benefactors they are grateful to their enemies ruthless. The disposition of the people is honest and simple.The history of Jihad: From Muhammad to ISIS. Ahmed Shah Durrani quoted in Smith, The Oxford History of India, 462.by one effort we get this thorn out of our sides for ever. The Marathas are the thorn of Hindostan.Sir Richard Temple quoted in Vikram Sampath - Savarkar, Echoes from a Forgotten Past, 1883–1924 (2019).It would be nearer the truth to say that it was the Mahrattas in the main, whom we displaced. It is commonly said that it was the Mahomedans whom the British displaced as rulers in India.The Marathas are credited to a large extent for ending Mughal rule in India. The empire formally existed from 1674 with the coronation of Chhatrapati Shivaji and ended in 1818 with the defeat of Peshwa Bajirao II. Siddi accepted a feudatory status under the Marathas.The Maratha Empire or the Maratha Confederacy was an Indian power that dominated much of the Indian subcontinent in the 17th and 18th century. A treaty was signed by the Marathas and Siddi. Chimajiappa, the younger brother of Bajirao Peshwa I, declared war against Siddi and won it. Therefore they could not pay much attention to the nuisance created by other enemies.ĭuring the times of Bajirao Peshwa I, (1733C.E.) once again the Marathas became active against Siddi. Hence, Maratha army stopped chasing Siddi.Īfter Chhatrapati Sambhaji Maharaj, Chhatrapati Rajaram Maharaj and Maharani Tarabai were continuously engaged in combating Aurangzeb. It would have been unwise to face two enemies on two different fronts. While Chhatrapati Sambhaji Maharaj, was thus planning to crush Siddi for ever, the Mughal army was marching toward Swarajya. Siddi was driven to despair because of the repeated attacks by the Marathas in the vicinity of Underi, Apte, Nagothane and Janjira. Hence, Chhatrapati Sambhaji Maharaj decided to curb his movement and planned a campaign against him. Siddi was increasingly getting difficult. In the end the British were forced to beat a retreat from the vicinity of Khanderi. 40- 50 small ships of the Marathas bravely confronted the British ships. The British deployed one big steamship and seven small ships. They seized British ships and captured a number of British officers. The British had to face strong opposition from Mainak Bhandari and Daulat Khan, the chief of Maratha navy. Hughes, a British officer attempted to shut down the construction work by stopping the supplies to the site. The construction work was supervised by Mainak Bhandari. To strengthen the Maratha position against these two, Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj began to build a fort on Khanderi island. Siddi and the British always helped each other against a common enemy. With the help of Mughals, Siddi successfully repulsed the Maratha army. Siddi, agreed to surrender the fort to Marathas but at the same time extended a hand of friendship to the Mughals and expessed readiness to be their feudatory. In 1671, Maratha army blocked all approaches to Janjira fort. Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj took over the forts at Tale, Ghosale and Rayari. In the latter half of the 15th century Siddi arrived in India from Abyssinia (Ethiopia). South Asian Association for Regional Co-operation (SAARC).Non-Alignment Policy of India and Non-Alignment Movement (NAM).Decolonisation to Political Integration of India - Puducherry.Decolonisation to Political Integration of India - Goa.Decolonisation to Political Integration of India - Dadra and Nagar-Haveli.Decolonisation to Political Integration of India.Mahatma Gandhi: Non-violent Resistance Movement.Founding of the Indian National Congress.Background of Founding the Indian National Congress.Contribution of the Rulers of Princely States in India.India and European Colonialism - French.India and European Colonialism - British.India and European Colonialism - Portuguese.Colonialism in Australia and New Zealand.Scientific Inventions in Various Fields.European Crusades and Its Farreaching Consequences.
Renaissance in Europe and Development of Science.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
